ERP Project Management: 7 Proven Strategies for Ultimate Success
Navigating ERP project management can be challenging, but with the right strategies, success is within reach. Discover how to streamline processes, avoid common pitfalls, and drive real business value through effective planning and execution.
Understanding ERP Project Management

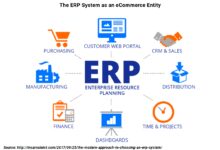
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) project management refers to the structured process of planning, executing, monitoring, and closing ERP implementation initiatives. These systems integrate core business functions—such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing—into a unified platform, enabling seamless data flow and improved decision-making across the organization.
Effective ERP project management ensures that the implementation aligns with strategic business goals, stays within budget, and delivers measurable ROI. According to Gartner, ERP systems are among the most complex software deployments a company can undertake, making skilled project management essential.
What Is ERP and Why It Matters
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning—a suite of integrated applications that manage day-to-day business activities. From order processing and procurement to inventory management and financial reporting, ERP systems centralize data and automate workflows.
The importance of ERP lies in its ability to eliminate data silos, reduce operational inefficiencies, and provide real-time visibility into business performance. A well-implemented ERP system can improve accuracy, enhance compliance, and support scalability.
Core Components of ERP Systems
Modern ERP platforms typically include several core modules, each designed to manage specific business functions:
- Financial Management: Handles general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Capital Management (HCM): Manages payroll, recruitment, performance reviews, and workforce planning.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Tracks procurement, inventory, logistics, and supplier relationships.
- Manufacturing: Supports production planning, quality control, and shop floor execution.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Integrates sales, marketing, and customer service operations.
These components work together within a single database, ensuring consistency and reducing redundancy. As noted by SAP, one of the world’s leading ERP vendors, integration is the key differentiator between ERP and standalone software solutions.
The Role of Project Management in ERP Success
ERP project management is not just about technical deployment—it’s about change management, stakeholder alignment, and strategic oversight. A project manager must coordinate cross-functional teams, manage timelines and budgets, mitigate risks, and ensure user adoption.
Without strong project leadership, even the most advanced ERP system can fail. Research from Panorama Consulting shows that nearly 60% of ERP projects exceed their initial budget, and 43% take longer than expected—often due to poor planning and inadequate project management.
“The success of an ERP implementation hinges not on the software itself, but on how well the project is managed from start to finish.” — Panorama Consulting Group
Key Phases of ERP Project Management
A successful ERP implementation follows a structured lifecycle. Each phase builds upon the previous one, ensuring a methodical approach that minimizes disruption and maximizes value. The typical ERP project management lifecycle includes five key stages: discovery and planning, design, development, deployment, and post-implementation support.
Following a phased approach allows organizations to identify risks early, validate requirements, and make informed decisions throughout the project. Let’s explore each phase in detail.
Phase 1: Discovery and Planning
This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire ERP project. It involves defining business objectives, identifying stakeholders, assessing current processes, and selecting the right ERP vendor and implementation partner.
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Key activities during this phase include:
- Conducting a business needs assessment
- Establishing project goals and KPIs
- Forming a project team with clear roles and responsibilities
- Developing a high-level project timeline and budget
- Evaluating ERP vendors through RFPs (Request for Proposals)
According to NetSuite, companies that invest time in thorough planning are 30% more likely to complete their ERP projects on time and within budget.
Phase 2: System Design and Configuration
Once the ERP platform is selected, the next step is to design the system architecture and configure it to meet organizational needs. This phase focuses on mapping current business processes to the ERP system’s capabilities.
Activities include:
- Process mapping and gap analysis
- Defining system workflows and approval hierarchies
- Customizing dashboards, reports, and user interfaces
- Setting up organizational structures (e.g., cost centers, departments)
It’s crucial to strike a balance between customization and standardization. Over-customization can lead to higher costs, longer timelines, and difficulties during upgrades. Best practice is to adapt business processes to fit the ERP system where possible, rather than forcing the system to conform to outdated workflows.
Phase 3: Development and Testing
This phase involves building any necessary customizations, integrating third-party systems, and migrating data from legacy platforms. It also includes rigorous testing to ensure system stability and data integrity.
Testing typically follows a multi-stage approach:
- Unit Testing: Validates individual components or modules.
- Integration Testing: Ensures different modules and external systems work together.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involves end-users verifying that the system meets business requirements.
- Performance Testing: Assesses system speed, scalability, and reliability under load.
Data migration is one of the most critical and risky aspects of this phase. Poor data quality or incomplete migration can undermine the entire implementation. A data cleansing strategy should be implemented before migration begins.
Common Challenges in ERP Project Management
Despite best efforts, ERP projects often face significant challenges. Recognizing these obstacles early allows organizations to proactively address them and increase the likelihood of success.
Understanding the root causes of ERP project failures is essential for any project manager. Let’s examine the most common issues and how to overcome them.
Lack of Executive Sponsorship
One of the top reasons ERP projects fail is insufficient support from senior leadership. Without active involvement from executives, it’s difficult to secure resources, drive change, and maintain momentum.
Executive sponsors play a vital role in communicating the vision, resolving conflicts, and reinforcing the importance of the project across departments. Their visibility and commitment help foster a culture of accountability and engagement.
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
To ensure strong sponsorship, involve C-level leaders from the outset, define their roles clearly, and provide regular progress updates. According to McKinsey, transformations with active executive sponsorship are 1.5 times more likely to succeed.
Poor Change Management
ERP implementations are as much about people as they are about technology. Employees often resist changes to familiar workflows, especially if they’re not involved in the process or don’t understand the benefits.
Effective change management includes:
- Communicating the ‘why’ behind the ERP initiative
- Engaging users early through workshops and feedback sessions
- Providing comprehensive training programs
- Establishing super-users or champions within departments
A study by Prosci found that projects with excellent change management are six times more likely to meet or exceed objectives than those with poor change management practices.
Scope Creep and Unrealistic Timelines
Scope creep—uncontrolled changes or continuous growth in project scope—is a major threat to ERP project success. It often results from unclear requirements, stakeholder pressure, or lack of governance.
Similarly, unrealistic timelines can lead to rushed implementations, skipped testing phases, and poor user adoption. To combat these issues:
- Define a clear project scope with documented requirements
- Establish a change control process to evaluate new requests
- Use realistic estimates based on industry benchmarks
- Break the project into manageable phases (e.g., pilot rollout)
Agile methodologies can be particularly effective in managing scope and delivering value incrementally.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Project Management
While ERP implementations are inherently complex, following proven best practices can dramatically improve outcomes. These strategies focus on people, processes, and technology to ensure a smooth and successful deployment.
Organizations that adopt these best practices report higher user satisfaction, faster time-to-value, and better alignment with strategic goals.
Assemble a Cross-Functional Project Team
A successful ERP project requires input from multiple departments. A cross-functional team ensures that all business units are represented and their needs are addressed.
The team should include:
- A dedicated project manager with ERP experience
- Business process owners from finance, HR, operations, etc.
- IT professionals responsible for infrastructure and security
- End-users who will interact with the system daily
This collaborative approach fosters ownership, improves decision-making, and enhances user buy-in.
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Define Clear Goals and KPIs
Before launching the project, establish clear, measurable objectives. These might include reducing invoice processing time by 30%, cutting inventory carrying costs by 15%, or improving financial close cycles.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be tracked throughout the project lifecycle to assess progress and demonstrate value. Examples include:
- Project budget variance
- Milestones achieved on time
- User adoption rates
- System uptime and performance
- Return on investment (ROI)
Regular reporting against these KPIs keeps the team focused and enables timely course corrections.
Leverage Agile and Iterative Approaches
Traditional waterfall models can be rigid and slow to adapt. In contrast, agile methodologies allow for iterative development, continuous feedback, and faster delivery of functional components.
For ERP project management, an agile approach might involve:
- Implementing one module at a time (e.g., finance first, then HR)
- Conducting sprints with defined deliverables
- Holding regular stand-up meetings to track progress
- Gathering user feedback after each release
This incremental strategy reduces risk, improves flexibility, and allows organizations to realize benefits sooner.
The Role of Technology in Modern ERP Project Management
Advancements in technology have transformed how ERP projects are managed. Cloud-based ERP systems, artificial intelligence, and real-time analytics are reshaping implementation strategies and outcomes.
Today’s ERP project management tools offer greater scalability, faster deployment, and enhanced collaboration capabilities.
Cloud ERP vs. On-Premise: What’s Best?
The choice between cloud and on-premise ERP has significant implications for project management. Cloud ERP solutions, such as Oracle NetSuite or Microsoft Dynamics 365, are hosted remotely and accessed via the internet.
Advantages of cloud ERP include:
- Faster implementation (often 30–50% quicker than on-premise)
- Lower upfront costs
- Automatic updates and patches
- Scalability and remote access
On the other hand, on-premise systems offer more control over data and customization but require significant IT infrastructure and longer deployment times.
According to IDC, over 70% of new ERP deployments are now cloud-based, reflecting a clear industry shift.
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
AI and Automation in ERP Implementation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotic process automation (RPA) are increasingly being used to streamline ERP implementations. AI-powered tools can analyze legacy data, suggest optimal configurations, and predict potential issues.
For example:
- AI-driven chatbots can assist with user training and support
- Machine learning algorithms can optimize inventory levels in real time
- RPA bots can automate data entry and reconciliation tasks
These technologies reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and accelerate time-to-value.
Real-Time Analytics and Dashboards
Modern ERP systems come equipped with powerful analytics engines that provide real-time insights into project performance and business operations.
Project managers can use dashboards to monitor:
- Implementation progress across modules
- Budget utilization and resource allocation
- User adoption trends and training completion rates
- System performance metrics (e.g., response time, error rates)
These insights enable proactive decision-making and help identify bottlenecks before they escalate.
Measuring the Success of ERP Project Management
Success in ERP project management isn’t just about going live on time and on budget. True success is measured by long-term business impact, user satisfaction, and sustained ROI.
Organizations must adopt a holistic approach to evaluation, combining quantitative metrics with qualitative feedback.
Financial and Operational Metrics
Quantitative KPIs provide objective evidence of ERP success. These include:
- Reduction in operational costs (e.g., labor, inventory)
- Improvement in order fulfillment cycle time
- Decrease in accounting errors or audit findings
- Increased revenue due to better forecasting and customer service
A study by Nucleus Research found that the average ROI for ERP systems is $4.21 for every dollar spent, with payback periods ranging from 12 to 18 months.
User Adoption and Satisfaction
No matter how powerful the system, it’s only effective if people use it. High user adoption is a key indicator of ERP success.
Ways to measure adoption include:
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Tracking login frequency and feature usage
- Conducting post-go-live surveys
- Monitoring help desk tickets related to usability
- Observing workflow efficiency improvements
Low adoption often signals issues with training, usability, or change management that need to be addressed promptly.
Long-Term Scalability and Flexibility
A successful ERP implementation should position the organization for future growth. The system should be able to scale with increasing transaction volumes, support new business units, and adapt to regulatory changes.
Indicators of long-term success include:
- Smooth integration with new applications (e.g., CRM, e-commerce)
- Ability to roll out the system to additional locations or subsidiaries
- Minimal disruption during upgrades or version changes
- Support for digital transformation initiatives (e.g., IoT, blockchain)
Organizations should conduct periodic ERP health checks to ensure the system continues to meet evolving business needs.
Future Trends in ERP Project Management
The landscape of ERP project management is evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies, shifting workforce expectations, and global business dynamics are shaping the next generation of ERP implementations.
Staying ahead of these trends allows organizations to future-proof their investments and maximize long-term value.
Hyperautomation and Intelligent ERP
Hyperautomation combines AI, RPA, and process mining to automate end-to-end business processes within ERP systems. This trend is moving ERP from a transactional system to a proactive, intelligent platform.
For example, intelligent ERP systems can:
- Predict cash flow shortages and recommend actions
- Automatically adjust production schedules based on demand forecasts
- Flag compliance risks in real time
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of organizations will use hyperautomation technologies to streamline operations and improve decision-making.
Low-Code/No-Code Customization
Modern ERP platforms are increasingly offering low-code or no-code development environments. These tools allow business users to create custom workflows, reports, and integrations without relying on IT.
Benefits include:
- Faster response to changing business needs
- Reduced dependency on technical teams
- Increased innovation at the departmental level
However, governance is critical to prevent uncontrolled customization that could compromise system integrity.
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Remote and Hybrid Implementation Models
The rise of remote work has transformed ERP project delivery. Many implementations are now conducted entirely virtually, using cloud collaboration tools and remote consulting services.
This shift offers several advantages:
- Access to global talent and expertise
- Reduced travel and on-site costs
- Greater flexibility in scheduling and resource allocation
However, it also requires stronger communication protocols, robust cybersecurity measures, and effective virtual training programs.
What is ERP project management?
ERP project management is the process of planning, executing, and overseeing the implementation of an Enterprise Resource Planning system. It involves coordinating people, processes, and technology to ensure the ERP system is deployed successfully, meets business objectives, and delivers long-term value.
How long does an ERP implementation typically take?
The duration varies based on complexity, but most ERP projects take between 6 to 18 months. Small businesses may complete implementations in 3–6 months, while large enterprises with complex processes can take 2+ years. Cloud-based ERP systems generally have shorter timelines than on-premise solutions.
What are the biggest risks in ERP project management?
Common risks include lack of executive sponsorship, poor change management, scope creep, data migration issues, inadequate training, and unrealistic timelines. These can lead to budget overruns, delays, low user adoption, and even project failure.
How can we improve user adoption after ERP implementation?
To boost adoption, organizations should invest in comprehensive training, involve users early in the design process, appoint departmental champions, communicate benefits clearly, and provide ongoing support. Gamification and interactive learning platforms can also enhance engagement.
Should we customize our ERP system or stick to standard processes?
erp project management – Erp project management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
It’s generally best to minimize customization and adapt business processes to fit the ERP system’s best practices. Excessive customization increases cost, complexity, and maintenance challenges. Use configuration options first, and only customize when absolutely necessary for competitive advantage.
ERP project management is a complex but rewarding endeavor. By understanding the key phases, addressing common challenges, adopting best practices, and leveraging modern technologies, organizations can achieve successful implementations that drive efficiency, visibility, and growth. The journey requires careful planning, strong leadership, and a focus on both technical and human factors. With the right approach, ERP systems can become a strategic asset that powers long-term business success.
Further Reading: