ERP Operations Management: 7 Powerful Strategies for Ultimate Efficiency
ERP operations management is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. By integrating core processes into a unified system, companies gain real-time insights, reduce redundancies, and boost productivity across departments.
What Is ERP Operations Management?

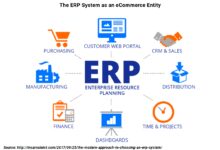
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) operations management refers to the strategic use of ERP systems to streamline, monitor, and optimize day-to-day business operations. These operations span across departments such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer service. An ERP system acts as the central nervous system of an organization, connecting disparate functions into a single source of truth.
Core Components of ERP Systems
Modern ERP platforms are built on a modular architecture, allowing businesses to adopt only the components they need. However, most comprehensive ERP systems include the following core modules:
Financial Management: Handles accounting, budgeting, asset management, and financial reporting.This module ensures compliance and provides real-time visibility into financial health.Investopedia explains how ERP financial modules reduce manual errors and accelerate closing cycles.Supply Chain Management (SCM): Manages procurement, inventory, logistics, and supplier relationships.With advanced forecasting tools, SCM modules help prevent stockouts and overstocking.Human Capital Management (HCM): Covers recruitment, payroll, performance management, and employee development.
.Integrated HCM ensures workforce planning aligns with operational goals.How ERP Enhances Operational VisibilityOne of the most transformative benefits of ERP operations management is the ability to achieve end-to-end operational visibility.Before ERP, data often lived in silos—sales in one system, inventory in another, finance in spreadsheets.This fragmentation led to delays, miscommunication, and poor decision-making..
With ERP, every transaction is logged in real time across the system. For example, when a sales order is placed, the inventory module automatically updates stock levels, the production module adjusts manufacturing schedules, and the finance module records revenue. This interconnectedness allows managers to see the ripple effects of every decision.
“A unified ERP system can reduce operational inefficiencies by up to 30%, according to a 2023 report by Gartner.”
This level of integration empowers leadership with dashboards and analytics that reflect the current state of the business, enabling proactive rather than reactive management.
Key Benefits of ERP in Operations Management
The implementation of ERP operations management brings a cascade of advantages that touch every corner of an organization. From cost reduction to improved customer satisfaction, the impact is both measurable and strategic.
Improved Process Efficiency
ERP systems automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and report generation. Automation not only reduces human error but also frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities. For instance, instead of manually reconciling purchase orders with invoices, the ERP system can match them automatically based on predefined rules.
According to a study by McKinsey, companies that automate core operations through ERP see a 20-25% increase in process efficiency within the first year of deployment.
- Reduction in manual data entry errors
- Faster order-to-cash and procure-to-pay cycles
- Streamlined interdepartmental workflows
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reporting
Data is the lifeblood of modern business decisions. ERP operations management ensures that data is not only accurate but also consistent across departments. Since all modules pull from the same database, there’s no discrepancy between what finance reports and what operations records.
Advanced reporting tools allow users to generate custom reports, KPIs, and real-time dashboards. For example, a logistics manager can pull a report showing on-time delivery rates, freight costs, and carrier performance—all from a single interface.
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
This accuracy is critical for compliance, auditing, and strategic planning. Regulatory bodies like the SEC and IRS require precise financial records, and ERP systems help maintain audit trails and version control automatically.
Scalability and Business Growth Support
As businesses grow, their operational complexity increases. Adding new locations, products, or markets can strain legacy systems. ERP operations management provides the scalability needed to support expansion without sacrificing control.
Cloud-based ERP solutions, in particular, offer elastic scalability. Companies can add new users, modules, or geographic instances with minimal downtime. For example, a manufacturer expanding into Europe can quickly configure multi-currency and multi-language settings within the ERP system.
SAP highlights that scalable ERP systems reduce the time to onboard new subsidiaries by up to 60%, enabling faster market entry.
ERP Operations Management in Manufacturing
Manufacturing is one of the most complex industries when it comes to operations management. From raw material procurement to production scheduling and quality control, the number of moving parts is immense. ERP operations management plays a pivotal role in bringing order to this complexity.
Production Planning and Scheduling
ERP systems enable manufacturers to create detailed production plans based on demand forecasts, available capacity, and material availability. The Master Production Schedule (MPS) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) modules are central to this process.
MRP calculates the exact quantity of raw materials needed for production, considering current inventory, open purchase orders, and lead times. This prevents over-ordering and minimizes carrying costs.
For example, an automotive parts manufacturer using ERP can automatically trigger a purchase order when inventory of a critical component drops below a safety threshold, ensuring uninterrupted production.
Inventory and Warehouse Management
Effective inventory management is crucial for maintaining service levels while minimizing costs. ERP operations management provides real-time visibility into stock levels across multiple warehouses, retail outlets, or distribution centers.
Features like barcode scanning, batch tracking, and FIFO (First In, First Out) management enhance accuracy and traceability. In industries like pharmaceuticals or food and beverage, where expiration dates matter, ERP systems can flag items nearing expiry and suggest redistribution or discounting strategies.
According to Oracle, companies using ERP for inventory management reduce excess stock by 20-35% and improve inventory turnover ratios significantly.
Quality Control and Compliance
In regulated industries, maintaining quality standards and compliance is non-negotiable. ERP systems support quality management by integrating inspection plans, non-conformance tracking, and corrective action workflows.
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
For instance, if a batch of products fails a quality test, the ERP system can automatically quarantine the batch, notify quality managers, and initiate a root cause analysis. It can also generate audit trails required for ISO or FDA compliance.
This level of control reduces the risk of recalls, enhances brand reputation, and ensures customer safety.
ERP in Supply Chain and Logistics
The supply chain is the backbone of any product-based business. ERP operations management transforms supply chain functions from reactive to proactive, enabling better coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers.
Demand Forecasting and Planning
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for aligning supply with market needs. ERP systems use historical sales data, market trends, and external factors (like seasonality or promotions) to predict future demand.
Advanced ERP platforms incorporate machine learning algorithms to refine forecasts over time. For example, a retail chain can use ERP to predict holiday sales spikes and adjust inventory levels across regions accordingly.
This predictive capability reduces the bullwhip effect—where small fluctuations in consumer demand cause large variations in orders upstream—leading to more stable supply chains.
Supplier Relationship Management
ERP operations management includes tools for evaluating, selecting, and managing suppliers. Vendor portals allow suppliers to view order status, update shipment details, and submit invoices directly into the ERP system.
Performance metrics such as on-time delivery rate, defect rate, and responsiveness are tracked and analyzed. Underperforming suppliers can be flagged for review, while top performers may be offered long-term contracts or incentives.
This transparency fosters stronger partnerships and reduces supply chain risks. A report by Deloitte found that companies with integrated supplier management in ERP experience 25% fewer disruptions.
Logistics and Distribution Optimization
ERP systems optimize logistics by integrating with transportation management systems (TMS) and warehouse management systems (WMS). This integration allows for route optimization, load planning, and real-time shipment tracking.
For example, a logistics manager can use ERP to compare carrier rates, select the most cost-effective option, and automatically generate shipping labels and customs documentation for international shipments.
Real-time GPS tracking feeds into the ERP system, allowing customer service teams to provide accurate delivery estimates. This level of service improves customer satisfaction and reduces inquiry volume.
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Financial Management Through ERP Operations
Finance is often the first department to adopt ERP, but its integration with operations is what unlocks true value. ERP operations management ensures that financial data reflects real-time operational activity, enabling better budgeting, forecasting, and cost control.
Real-Time Financial Reporting
Traditional financial reporting often suffers from delays—monthly close processes can take weeks. ERP operations management changes this by providing real-time financial statements.
Every transaction—whether it’s a sale, purchase, or payroll run—is immediately reflected in the general ledger. CFOs can access up-to-date balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports at any time.
This immediacy supports faster decision-making. For instance, if a major customer delays payment, the finance team can see the impact on cash flow instantly and adjust credit terms or financing strategies accordingly.
Cost Accounting and Profitability Analysis
ERP systems enable detailed cost accounting by tracking direct and indirect costs across products, projects, or departments. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) modules allocate overhead costs more accurately than traditional methods.
A manufacturer can determine the true cost of producing a specific product line, including labor, materials, machine time, and overhead. This insight helps identify unprofitable products and optimize pricing strategies.
Profitability analysis can be drilled down by region, customer segment, or sales channel. For example, an e-commerce company might discover that while overall sales are growing, profitability is declining in a specific geographic market due to high shipping costs—information that would be difficult to uncover without ERP integration.
Budgeting and Forecasting Integration
ERP operations management bridges the gap between operational plans and financial forecasts. Sales projections from the CRM module feed directly into the financial planning module, allowing for dynamic budgeting.
Scenario planning tools let finance teams model different outcomes—such as a 10% increase in raw material costs or a new product launch—and assess their financial impact. This proactive approach reduces surprises and improves strategic agility.
According to PwC, companies with integrated ERP financial planning are 30% more likely to meet or exceed earnings targets.
Human Resources and ERP Operations Management
People are the most valuable asset in any organization, and ERP operations management extends its reach into human resources to ensure workforce alignment with business goals.
Workforce Planning and Talent Management
ERP HCM modules provide tools for strategic workforce planning. HR managers can analyze current skill sets, forecast future needs based on operational plans, and identify gaps.
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
For example, if a company plans to launch a new product line requiring specialized technicians, the ERP system can flag the need for recruitment or training programs. Succession planning features help identify high-potential employees for leadership roles.
This proactive approach reduces hiring delays and ensures that the right talent is in place when needed.
Payroll and Compliance Automation
Payroll processing is complex, especially for multinational companies dealing with different tax codes, labor laws, and currencies. ERP systems automate payroll calculations, tax withholdings, and regulatory filings.
Integration with time and attendance systems ensures that employee hours are accurately recorded and paid. Leave balances, overtime, and bonuses are all managed within the same platform.
This automation reduces compliance risks and audit exposure. In the U.S., for instance, ERP systems can automatically generate W-2 forms and file them with the IRS, minimizing errors and penalties.
Employee Self-Service and Engagement
Modern ERP systems include employee self-service portals where staff can update personal information, request time off, view payslips, and enroll in benefits—all without HR intervention.
This not only reduces administrative burden but also improves employee satisfaction. A study by IBM found that companies with self-service HR tools report 20% higher employee engagement scores.
Additionally, performance management modules allow for continuous feedback, goal setting, and 360-degree reviews, fostering a culture of growth and accountability.
Choosing the Right ERP System for Operations Management
Selecting the right ERP system is a critical decision that can shape a company’s operational efficiency for years to come. The process requires careful evaluation of business needs, scalability, integration capabilities, and total cost of ownership.
On-Premise vs. Cloud ERP Solutions
One of the first decisions is whether to go with an on-premise or cloud-based ERP system. On-premise solutions require significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT staff. They offer full control over data and customization but can be costly to maintain and upgrade.
Cloud ERP, on the other hand, is hosted by the vendor and accessed via the internet. It typically follows a subscription model (SaaS), reducing upfront costs and enabling faster deployment. Cloud ERP also benefits from automatic updates and built-in security.
According to Gartner, over 70% of new ERP implementations in 2023 were cloud-based, driven by flexibility and lower TCO.
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
While generic ERP systems work for many businesses, industry-specific solutions offer tailored functionality. For example:
- Discrete Manufacturing: Requires detailed bill of materials (BOM) and shop floor control.
- Process Manufacturing: Needs batch tracking, formula management, and compliance with FDA or USDA regulations.
- Retail: Benefits from omnichannel inventory, POS integration, and customer loyalty programs.
Choosing an ERP system designed for your industry ensures that critical processes are supported out of the box, reducing customization and implementation time.
Vendor Evaluation and Implementation Strategy
When evaluating ERP vendors, consider factors such as:
- Proven track record in your industry
- Strength of customer support and training
- Integration capabilities with existing systems (CRM, e-commerce, etc.)
- User interface and ease of adoption
Implementation strategy is equally important. A phased rollout—starting with finance and inventory, then expanding to HR and manufacturing—reduces risk and allows teams to adapt gradually.
Engaging a certified implementation partner can significantly improve success rates. Deloitte reports that companies using experienced consultants are 50% more likely to complete ERP projects on time and within budget.
Future Trends in ERP Operations Management
ERP operations management is not static—it evolves with technology and business needs. Emerging trends are reshaping how companies use ERP to gain competitive advantage.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming ERP from a transactional system into a predictive and prescriptive platform. AI-powered ERP can forecast demand, detect anomalies in financial transactions, and recommend optimal production schedules.
For example, AI can analyze historical data to predict machine failures before they occur, enabling preventive maintenance and reducing downtime. This is known as predictive maintenance, and it’s becoming a standard feature in modern ERP systems.
Vendors like Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Oracle AI are embedding machine learning models directly into their ERP suites.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Real-Time Monitoring
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables physical devices—machines, vehicles, sensors—to connect to the ERP system and send real-time data. In a smart factory, sensors on production lines can transmit temperature, pressure, and output rates directly into the ERP system.
This real-time monitoring allows for immediate adjustments. If a machine is operating outside optimal parameters, the ERP system can alert maintenance teams or automatically adjust settings via integration with SCADA systems.
IoT integration enhances quality control, reduces waste, and improves energy efficiency—key goals in sustainable manufacturing.
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is being explored to enhance supply chain traceability within ERP systems. By recording every transaction on an immutable ledger, blockchain ensures that product origins, certifications, and shipment histories cannot be altered.
For example, a food company can use blockchain-integrated ERP to trace a contaminated product back to its source farm in seconds, rather than days. This capability is crucial for recalls and brand protection.
While still in early adoption, blockchain-ERP integration is gaining traction in industries like pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and agriculture.
What is ERP operations management?
ERP operations management refers to the use of Enterprise Resource Planning systems to integrate, automate, and optimize core business processes such as finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and HR. It provides a unified platform for real-time data sharing and decision-making across departments.
How does ERP improve operational efficiency?
ERP improves efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, eliminating data silos, reducing manual errors, and providing real-time insights. This leads to faster decision-making, lower operational costs, and improved resource utilization across the organization.
What are the main challenges in ERP implementation?
Common challenges include high upfront costs, resistance to change from employees, data migration issues, and inadequate training. To overcome these, companies should adopt a phased implementation approach, involve stakeholders early, and invest in change management.
Can small businesses benefit from ERP operations management?
Absolutely. Cloud-based ERP solutions are scalable and affordable, making them accessible to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). These systems help SMBs streamline operations, improve customer service, and compete more effectively with larger players.
What is the future of ERP in operations management?
erp operations management – Erp operations management menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The future of ERP lies in AI, IoT, and blockchain integration. These technologies will enable predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and enhanced supply chain transparency, transforming ERP from a back-office system into a strategic decision-making engine.
In conclusion, ERP operations management is a powerful enabler of business efficiency, agility, and growth. By integrating core functions into a single platform, organizations gain real-time visibility, reduce costs, and improve decision-making. Whether in manufacturing, supply chain, finance, or HR, ERP systems provide the tools needed to navigate complexity and drive performance. As technology evolves, the role of ERP will only become more strategic, making it an indispensable asset for any forward-thinking business.
Further Reading: