Enterprise Resource Planning: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
If you’ve ever wondered how large organizations manage their complex operations seamlessly, the answer often lies in enterprise resource planning. It’s the digital backbone that ties everything together—finance, HR, supply chain, and more.
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning?

Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a type of software system that integrates core business processes into a single, unified platform. Instead of having separate systems for accounting, inventory, human resources, and customer management, ERP brings them all under one roof. This integration allows data to flow smoothly across departments, reducing redundancy, improving accuracy, and enhancing decision-making.
The Evolution of ERP Systems
ERP didn’t start as the sophisticated cloud-based platforms we see today. Its roots go back to the 1960s with inventory management systems in manufacturing. By the 1970s, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems emerged, helping companies plan production and manage raw materials more efficiently. In the 1980s, MRP evolved into MRP II, which included additional functions like scheduling and capacity planning.
The term “enterprise resource planning” was coined by Gartner in 1990, marking a shift toward integrated systems that could handle multiple business functions across departments and even global locations. Since then, ERP systems have evolved dramatically, incorporating advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing.
- 1960s: Basic inventory control systems
- 1970s: Introduction of MRP for manufacturing
- 1980s: MRP II adds scheduling and shop floor control
- 1990s: True ERP systems emerge with cross-functional integration
- 2000s: Web-based ERP and broader adoption
- 2010s–Present: Cloud ERP, mobile access, AI, and IoT integration
“ERP is not just a software solution; it’s a strategic enabler of business transformation.” — Gartner Research
How ERP Differs From Traditional Software
Traditional business software often operates in silos. For example, your sales team might use one system, finance another, and logistics a third. This fragmentation leads to data duplication, communication gaps, and inefficiencies. ERP breaks down these silos by centralizing data and processes.
Unlike standalone applications, ERP systems are designed with a common database and consistent user interface. This means when a sales order is entered, it automatically updates inventory levels, triggers billing, and informs the shipping department—all in real time. This level of automation and integration is what sets ERP apart.
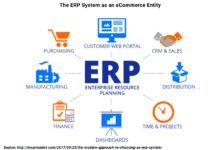
Core Components of an ERP System
A typical ERP system consists of several interconnected modules, each designed to manage a specific business function. While the exact modules vary by vendor and industry, most ERP platforms include the following core components:
- Financial Management: Handles general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources (HR): Manages employee data, payroll, benefits, recruitment, and performance reviews.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Tracks procurement, inventory, warehousing, and logistics.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Supports sales, marketing, and customer service activities.
- Manufacturing: Includes production planning, quality control, and shop floor management.
- Project Management: Enables planning, tracking, and billing for projects.
These modules share a common database, ensuring that changes in one area are instantly reflected across the system. For instance, when a product is shipped, the inventory module updates stock levels, the finance module records revenue, and the CRM module notifies the customer—all automatically.
Why Enterprise Resource Planning Is Essential for Modern Businesses
In today’s fast-paced, data-driven world, businesses can’t afford to rely on disconnected systems and manual processes. Enterprise resource planning provides the infrastructure needed to operate efficiently, scale effectively, and respond quickly to market changes. Whether you’re a small growing company or a multinational corporation, ERP can be a game-changer.
Breaking Down Data Silos
Data silos occur when information is isolated within departments, making it difficult to access and analyze across the organization. For example, if marketing doesn’t know what inventory is available, they might promote products that are out of stock. ERP eliminates these silos by centralizing data, giving every authorized user access to the same real-time information.
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
This transparency improves coordination and reduces errors. A study by Nucleus Research found that companies using ERP systems reduce data entry errors by up to 50%. With everyone working from the same data set, decisions are more accurate and consistent.
Improving Operational Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of enterprise resource planning is increased efficiency. By automating routine tasks like invoice processing, payroll, and order fulfillment, ERP frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
For example, instead of manually entering purchase orders into multiple systems, an ERP user can generate and approve them with a few clicks. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of human error. According to a report by Panorama Consulting, organizations that implement ERP systems see an average productivity increase of 22%.
Enabling Real-Time Decision Making
In the past, business leaders often made decisions based on outdated reports generated days or even weeks after the fact. With ERP, executives can access real-time dashboards and analytics that provide up-to-the-minute insights into key performance indicators (KPIs).
For instance, a CEO can log in and instantly see sales trends, inventory levels, and cash flow status. This ability to monitor business performance in real time allows for faster, more informed decisions. A survey by Aberdeen Group found that best-in-class companies using ERP are 2.5 times more likely to report improved decision-making capabilities.
Key Features of Modern Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
Today’s ERP systems are far more advanced than their predecessors. They are not just about integrating business processes—they also offer powerful tools for analytics, collaboration, and innovation. Let’s explore some of the most important features that define modern ERP platforms.
Cloud-Based Deployment
One of the biggest shifts in ERP over the last decade has been the move to the cloud. Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet, eliminating the need for expensive on-premise hardware and IT staff.
Cloud ERP offers several advantages, including lower upfront costs, faster implementation, automatic updates, and greater scalability. Companies like SAP and Oracle now offer robust cloud ERP solutions that serve businesses of all sizes.
Additionally, cloud ERP enables remote work and mobile access, which became crucial during the global shift to hybrid work models. Employees can access the system from anywhere, on any device, ensuring business continuity.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming enterprise resource planning by adding predictive and prescriptive capabilities. For example, AI-powered ERP systems can forecast demand more accurately, detect anomalies in financial transactions, and recommend optimal inventory levels.
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Microsoft Dynamics 365, for instance, uses AI to provide intelligent recommendations for sales teams, such as which leads are most likely to convert. Similarly, Infor integrates AI into its ERP suite to automate invoice matching and reduce processing times.
These intelligent features not only improve accuracy but also reduce the workload on employees, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives rather than repetitive tasks.
Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence
Modern ERP systems come equipped with powerful analytics tools that turn raw data into actionable insights. Dashboards, reports, and data visualizations help managers track performance, identify trends, and spot potential issues before they escalate.
For example, a retail company can use ERP analytics to analyze sales by region, product category, and customer segment. This information can inform marketing strategies, inventory planning, and pricing decisions.
Many ERP vendors partner with business intelligence platforms like Power BI or Tableau to enhance their reporting capabilities. This integration allows users to create custom reports and drill down into data without needing technical expertise.
Types of Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
Not all ERP systems are created equal. Depending on the size, industry, and specific needs of a business, different types of ERP solutions are available. Understanding these types can help organizations choose the right system for their goals.
On-Premise ERP
On-premise ERP systems are installed and run on the company’s own servers and computers. This gives organizations complete control over their data and infrastructure, which is often preferred by large enterprises with strict security and compliance requirements.
However, on-premise ERP requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT personnel. Maintenance, upgrades, and backups are the responsibility of the company, which can be resource-intensive.
Despite the higher costs, some industries—such as defense, healthcare, and finance—still favor on-premise solutions due to data sovereignty and regulatory concerns.
Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP, also known as SaaS (Software as a Service) ERP, is hosted by the vendor and accessed over the internet. This model has gained immense popularity due to its affordability, scalability, and ease of use.
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
With cloud ERP, businesses pay a subscription fee instead of a large upfront cost. The vendor handles maintenance, security, and updates, reducing the burden on internal IT teams. Companies like NetSuite and Workday are leaders in the cloud ERP space.
Cloud ERP is especially beneficial for small and mid-sized businesses that want to implement ERP without heavy capital investment. It also supports rapid scaling—companies can easily add users or modules as they grow.
Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP combines elements of both on-premise and cloud systems. Some modules run locally, while others are hosted in the cloud. This approach offers flexibility, allowing companies to keep sensitive data on-premise while leveraging the cloud for less critical functions.
For example, a manufacturer might keep its production planning module on-premise for real-time control but use a cloud-based CRM for sales and marketing. Hybrid ERP is ideal for organizations undergoing digital transformation and transitioning gradually from legacy systems.
Industries That Benefit Most From Enterprise Resource Planning
While ERP systems can be valuable across sectors, certain industries gain particularly significant advantages due to their operational complexity and regulatory demands. Let’s explore how different industries leverage enterprise resource planning to drive success.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers face challenges like supply chain volatility, production scheduling, quality control, and compliance. ERP systems help streamline these processes by integrating production planning, inventory management, and procurement.
For example, an ERP system can automatically adjust production schedules based on real-time demand forecasts and material availability. It can also track product quality throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring compliance with industry standards like ISO 9001.
Companies like Siemens and General Electric use ERP to manage global operations, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
Retail and E-Commerce
Retailers must manage inventory across multiple channels—brick-and-mortar stores, online platforms, and third-party marketplaces. ERP systems provide a unified view of inventory, sales, and customer data, enabling omnichannel retailing.
With ERP, retailers can prevent stockouts, optimize pricing, and personalize customer experiences. For instance, when a customer buys a product online, the ERP system instantly updates inventory levels across all channels, preventing overselling.
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
E-commerce giants like Amazon and Shopify rely on sophisticated ERP-like systems to manage millions of transactions daily and maintain high service levels.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations deal with complex billing, patient records, regulatory compliance, and supply chain management. ERP systems help hospitals and clinics streamline administrative processes, reduce costs, and improve patient care.
An ERP system in healthcare can integrate patient scheduling, billing, pharmacy management, and human resources. This integration reduces paperwork, minimizes billing errors, and ensures compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
For example, the Mayo Clinic uses ERP to manage its financial and operational data, enabling better resource allocation and strategic planning.
Challenges and Risks in Enterprise Resource Planning Implementation
Despite its many benefits, implementing an enterprise resource planning system is not without challenges. Many organizations underestimate the complexity involved, leading to delays, cost overruns, and user resistance. Understanding these risks is crucial for a successful ERP rollout.
High Implementation Costs
ERP implementation can be expensive, especially for on-premise systems. Costs include software licenses, hardware, consulting fees, training, and ongoing maintenance. According to Panorama Consulting, the average ERP project costs between $150,000 and $750,000 for mid-sized companies.
Cloud ERP reduces upfront costs but may lead to higher long-term expenses due to subscription fees. Organizations must carefully evaluate their budget and choose a solution that offers the best return on investment.
Data Migration Issues
Migrating data from legacy systems to a new ERP platform is one of the most complex aspects of implementation. Data may be incomplete, inconsistent, or stored in incompatible formats, leading to errors and downtime.
A well-planned data migration strategy is essential. This includes data cleansing, validation, and testing. Companies should also establish data governance policies to ensure data quality after go-live.
User Resistance and Change Management
Employees often resist ERP systems because they fear job loss, dislike change, or find the new system difficult to use. Without proper change management, even the best ERP system can fail.
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Successful implementations involve clear communication, comprehensive training, and involvement of end-users in the design process. Leadership must champion the change and demonstrate the benefits of the new system.
A study by McKinsey found that 70% of change programs fail due to lack of employee engagement. Investing in change management is not optional—it’s a critical success factor.
Future Trends in Enterprise Resource Planning
The world of enterprise resource planning is evolving rapidly. As technology advances and business needs change, ERP systems are becoming more intelligent, flexible, and user-friendly. Let’s look at some of the key trends shaping the future of ERP.
AI-Driven Automation
Artificial intelligence will continue to play a larger role in ERP. Future systems will use AI not just for analytics but for full process automation. For example, AI could automatically approve low-risk purchase orders, reconcile invoices, or detect fraud in real time.
As natural language processing improves, users may interact with ERP systems using voice commands or chatbots, making the software more accessible to non-technical staff.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The IoT is connecting physical devices to digital systems, and ERP is no exception. In manufacturing, sensors on machines can send real-time data to the ERP system, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
In logistics, GPS-enabled trackers can update ERP systems with shipment locations, improving delivery accuracy and customer satisfaction. As IoT adoption grows, ERP will become even more integrated with the physical world.
Blockchain for Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology offers a secure, tamper-proof way to record transactions. In ERP, blockchain can be used to verify the authenticity of supply chain data, prevent fraud, and ensure compliance.
For example, a food company could use blockchain within its ERP system to track the origin of ingredients, ensuring food safety and building consumer trust. While still in early stages, blockchain integration is expected to grow in the coming years.
What is enterprise resource planning?
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a software system that integrates core business processes—such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing—into a single platform. It enables real-time data sharing across departments, improving efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making.
What are the main benefits of ERP?
The main benefits of enterprise resource planning include improved operational efficiency, real-time visibility into business performance, reduced data silos, better compliance, and enhanced decision-making through advanced analytics.
How much does an ERP system cost?
The cost of an ERP system varies widely based on size, deployment model, and vendor. Small businesses might pay $10,000–$50,000 for cloud ERP, while large enterprises can spend millions on on-premise solutions. Ongoing costs include subscriptions, maintenance, and training.
How long does ERP implementation take?
Implementation time depends on the complexity of the system and organization. Small businesses may go live in 3–6 months, while large enterprises can take 12–24 months or more. Proper planning, data migration, and user training are critical for timely deployment.
Is cloud ERP secure?
Yes, cloud ERP is generally secure. Reputable vendors use encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits to protect data. In many cases, cloud providers offer better security than on-premise systems due to their specialized expertise and infrastructure.
Enterprise resource planning is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for organizations that want to stay competitive in a digital world. From breaking down data silos to enabling real-time decision-making, ERP systems provide the foundation for operational excellence. While implementation can be challenging, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. As technology continues to evolve, ERP will become even more intelligent, connected, and essential. Whether you’re a small startup or a global enterprise, investing in the right ERP solution can transform the way you do business.
enterprise resource planning – Enterprise resource planning menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: